What is Electronic Device ???
Perhaps this is a very basic question in this very modern era. The rapid development of technology with rapid advances makes the electronic device can be found almost every corner of the earth.
Before going any further, it's good we understand first what is electronic.
Electronic
The word electronics itself comes from the word electrons that are part of the atom. Electrons are part of a negatively charged sub-atom. Electron itself comes from the Greek word, elektron, which this word stands for amber in Greek words.
Electronic itself is a branch of electrical science. Electronic is a study of weak current electric devices used by controlling the flow of electrons in a device such as computers, electronic equipment, thermocouples, semiconductors and so forth.
Tracing back to the past, the development of electronics began in the 20th century where the first electronic device was a vacuum tube (thermionic tube). The development of the history of electronics can be described as follows:
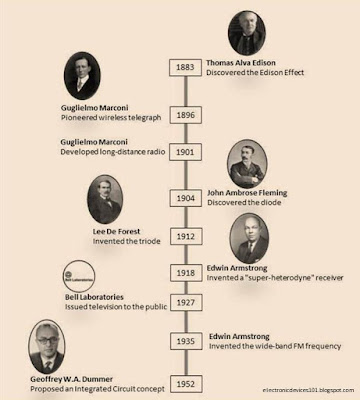
- In 1883 Thomas Alva Edison discovered that electrons can move between conductors by passing through a vacuum. This phenomenon is then called the Edison Effect.
- In 1896, Guglielmo Marconi pioneered the development of wireless telegraph.
- In 1901, Guilgelmo Marconi developed long-distance radio communication.
- In 1904, John Ambrose Fleming applied the Edison Effect in his experiment which later discovered the diode.
- In 1912, Lee De Forest invented the triode.
- In 1918, Edwin Armstrong invented a "super-heterodyne" receiver capable of selecting radio signals and can receive long-distance signals.
- In 1927, Bell Laboratories issued television to the public, and this is still an electromechanical form. But Vladimir Zworykin, an engineer at Radio Corporation of America (RCA), is considered the "father of television" because of his invention, the picture tube and the iconoscope camera jar.
- In 1935, Edwin Armstrong invented the wide-band FM frequency modulation.
- In the mid-1950s, television has passed the radio for home use and entertainment.
- In 1952, Geoffrey W.A. Dummer, proposed an Integrated Circuit concept.
- In 1961, Integrated Circuit (IC) became fully produced by a number of companies.
We can see that electronics have developed quite rapidly and involve many experts and institutions.
As described earlier, electronics are derived from the word electron. In other words, we can conclude that electronic devices take advantage of electrons in their work processes.
Electron is a form of energy. The electricity we use every day is the electron itself. The electric current we know is the amount of electrical charge caused by the movement of electrons flowing in a network per unit of time. Electrons are negatively charged. Electrons can cause the process of magnetism, thermal conductivity and even photons (light energy). Electrons as energy can be transformed into another energy forms. These electron energy properties are then utilized by conductors and semiconductors for the delivery of information analogue or digital in electronic devices.
Electronic Device Components
Electronic device consists of several components that have their respective roles - each.
There are two major categories of electronic components i.e. active components and passive components. The electronic active component is an electronic component that can work when it gets an electric current. While the electronic passive component is an electronic component that does not require an electric current to work, the work process is passive to electric current, the component has no amplifier or rectifier function such as active component.
In general, the components that must exist and are often found in electronic devices are as follows:
1. Resistor
Resistor is a passive electronic component that serves to inhibit and regulate electrical current in an electronic circuit. The unit of resistor value is Ohm (Ω). Resistor values are usually represented by Code numbers or color bracelets contained in the body of the resistor.
The types of resistors are:
- Resistor with fixed values
- Resistor with adjustable values, these types of resistors are often referred to as variable resistor or potentiometer.
- Resistor with values can change according to light intensity, this type of resistor is called the LDR or Light Dependent Resistor
- Resistor whose value may change according to the temperature change, this type of resistor is called PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) and NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient
Resistor illustration
2. Capacitor
The capacitor or also called the condenser is a passive electronic component that can store energy or electrical charge in the interim. Capacitor functions include being able to select radio waves in the tuner circuit, as a gradient of current on the rectifier and also as a filter in the power supply circuit. The unit of value for capacitor is Farad (F)
Types of capacitor include:
- Capacitor with fixed values and non-polarity.
- Capacitor with fixed values but have positive and negative polarity.
- Capacitor with adjustable values, This type of capacitor is often called the variable capacitor.
 |
| Source: http://www.pinball.center/media/image/image_02525_1.jpg |
Capacitor
3. Inductor
An inductor also called a coil is a passive electronic component that functions as a frequency regulator, filter and also as a connector. Inductor are commonly found in electronics-related equipment or circuits such as tuners for radio planes. The unit of inductance for the inductor is Henry (H).
The types of inductor are:
- Inductor with fixed value
- Inductor with adjustable value or called variable coil.
 |
| Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inductor |
4. Diode
Diode is an active electronics component that serves to conduct an electric current in one direction and to inhibit electric current from the opposite direction. The diode consists of two electrodes i.e. anode and cathode.
Based on its function, diodes are classified as follows:
- Common diode or rectifier diode generally made of silicon and serves as an alternating current rectifier (AC) to direct current (DC).
- Zener diode that serves as a security circuit after the voltage determined by the Zener diode in question. The voltage is often called the Zener voltage.
- Light Emitting Diode (LED) is a diode that can emit monochromatic light.
- Photo diode ie light-sensitive diode so often used as a sensor.
- Schottky diode (SCR or Silicon Control Rectifier) is a diode that acts as a controller.
- Laser diode is a diode that can radiate laser light. Laser diodes are generally abbreviated as LD.
 |
| Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inductor |
5. Transistor
Transistor is an active electronics component that has many functions and is a component that plays a very important role in this modern electronic world.
Some functions of transistors such as current amplifier, as a switch (breaker and connector), voltage stabilization, signal modulation, rectifier and so forth.
Transistors consist of 3 terminals of base (B), emitter (E) and collector (K). Based on the structure, the transistor consists of two types of structures, namely PNP and NPN. Union Junction Transistors (UJT), Field Effect Transistors (FET) and Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effects Transistors (MOSFET) are also part of the transistor type.
 |
| Source: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/transistors |
Source :
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_component
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Electronic/rescarb.html
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/transistors